Recently, the Center's Fishery Environmental Protection Research Team made a new progress on the structure of planktonic bacterial communities and its response to some biological and abiotic factors in fish ponds. Related achievements was published online in the top journal Environmental Pollution (real-time impact factor 5.714). Full text URL: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113656.
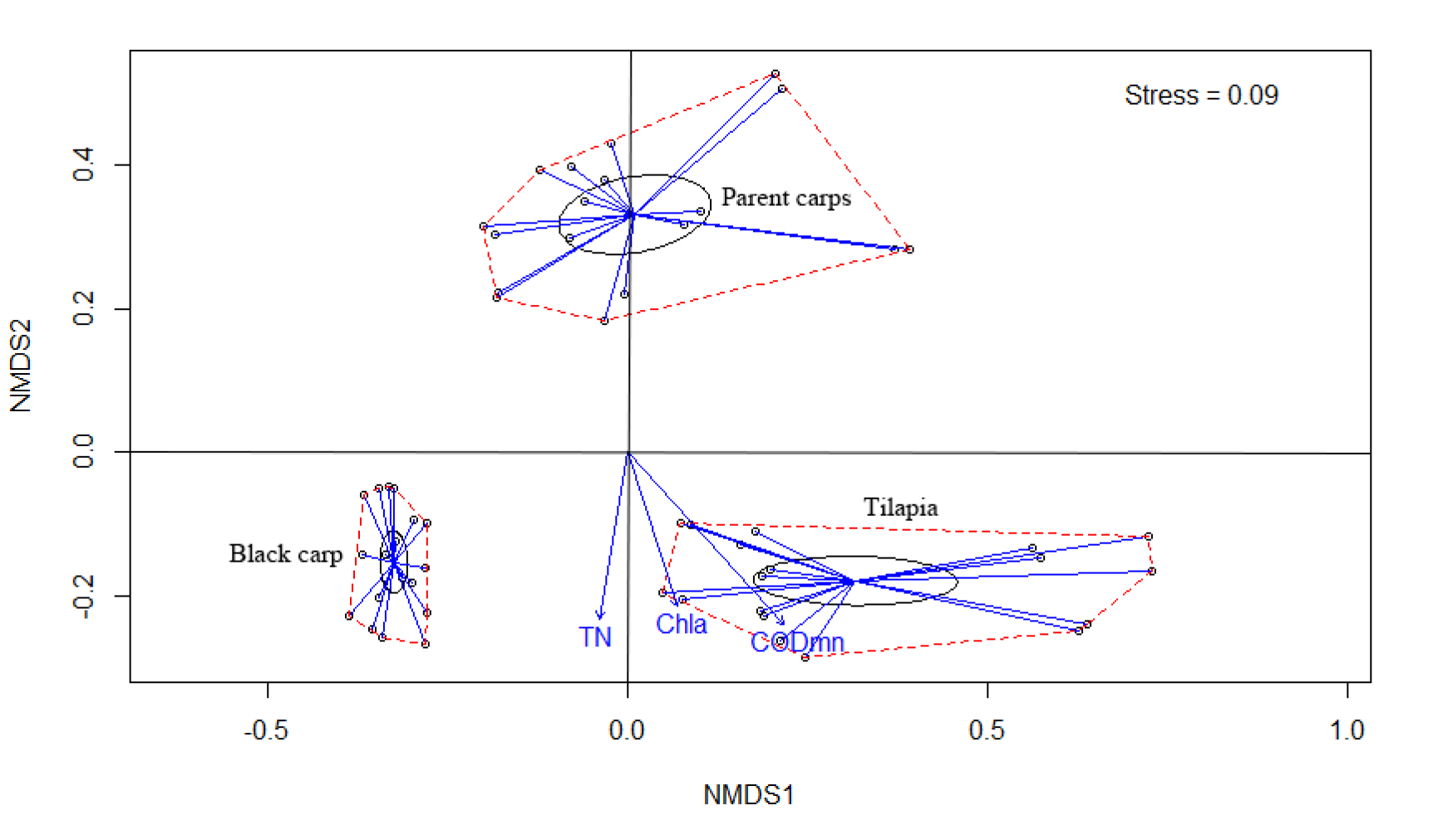
This study analyzed samples from different ponds and different water layers at the peak of farming. Starting from aspects of bacterial community composition and β diversity, multivariate analysis of variance was used to explore influencing factors of phytoplankton community in freshwater culture pond systems. Studies have shown that biological differences between different cultured species are the main factors that cause differences in the structure of planktonic communities in the water; the relationship is closebetween the permanganate index, the combination of chlorophyll a and total nitrogen, and the β diversity of planktonic bacteria in physical and chemical factors, of which the permanganate index is the most important influencing factor; the algae-bacteria symbiosis relationship plays an important role in the process of material cycling in freshwater ponds during the peak culture period.